



What Do Consultants Do?
Today, everybody is a consultant. You can be a legal consultant, a public relations consultant, social media consultant, and for us, it can be Strategy consulting, operational consulting, or interim. And depending on that, we will be involved, or not. But what do consultants do exactly?
What is a Consultant?
The word "consultare" comes from Latin, and it means to "consult, advise." Since the beginning of time -- well, at least of economic activity and established societal structures, people have looked for ways to better manage their business affairs and make more effective decisions.
What exactly is a consultant? This is what you can find in a dictionary:
con•sult•ant (kənˈsʌltnt)
- Provides professional and expert advice to another person or an entity.
- Receives compensation for the service he or she provided.
As you can see, consulting is often defined as giving expert advice to other professionals. True, but it is a bit simplistic. Because sometimes the consultants don’t give advice: they do the work. You can find consultants all over professional services spanning legal, engineering, investment, advertising, and general management services.
In this article, we’ll explore who management consultants are? What are the different types of consultants? And what do they do?
What are the Different Types of Management Consultants?
The consulting industry is one of the most diverse industries there is, and, hence, there are a number of different types of consultants. Given the wide area in which a consultant can work, and variety of work place a consultant can access, there has been a sharp rise in the number of independent consultants over the past few years. Following wide influx into the industry, a common definition of a consultant has become harder to reach.
There is actually just one broader term in consulting which is “Management consulting”. We have developed a template to include the main consulting capabilities in 7-High Level categories:
Strategy & Management
Strategy is about building a competitive advantage among the competition and make profits. As a result, the capability is geared toward high-level, corporate decisions. It helps leaders define “where to play” and “how to win” for achieving a financial return. A significant share of high-level Consulting engagements falls in this category.
This category includes capabilities such as Corporate Strategy, Business Unit Strategy, Organization Architecture, Management Model, Corporate Governance, Innovation Strategy, M&A, Strategic Communication as well as Economic or Government Policy.
Sales & Marketing
Sales & Marketing is focused on top-line activities to help companies drive profitable growth. Sales & marketing consultants support clients to deliver above-market growth by developing their marketing capabilities or improving their sales effectiveness.
This category includes capabilities such as Branding, Revenue Management, Market Entry Strategy, Omni Channel Marketing, Sales Effectiveness or Customer Experience.
Operations
Operations are one of the largest lines of services. It regroups most of the activities where products and services are usually built or delivered. Even though Operations can be a source of innovation and a differentiator, most of the time the focus is on reducing costs and increasing throughout.
Operations consultants use concepts such as Lean, Six Sigma, or Quality Management to help their clients streamline and improve operational efficiency. It represents about 25% of the market for management consulting.
The category includes capabilities such as Manufacturing, Procurement, Supply chain, Quality Management, and Compliance, G&A Optimization, Lean or Knowledge Management.
Finance & Risk
Consulting firms specialized in financial advisory service work with finance and risk management executives (such as CFO’s). They help them make decisions, develop customized strategies and deliver superior results by analyzing the financial and economic risk and uncertainties for their companies. The category represents close to 20% of the management consulting industry.
The category includes capabilities such as Corporate Finance, Actuarial, Restructuring and Crisis Management, Tax Advisory or Risk Management.
Human Capital
Human Capital consulting focuses on maximizing the value created from Human Resources, or employees, in an organization. The offering is quite wide from Organization and Leadership Development to Improving the Effectiveness of the HR function.
The category includes capabilities such as Talent Management, Organization Development, HR Effectiveness, Social Relations or Compensations & Benefits.
Research & Development
Research & Development Consulting is helping companies to optimize the way they are developing Products and Services. Companies aim to find the right balance between with a strong focus on customer needs and delivering cost-effective returns. In a time of constant change and when innovation cycles are accelerating, the research and development activities have become a key differentiator.
The category includes capabilities such as R&D Strategy, R&D Effectiveness, Product Development, Manufacturing Engineering, Open Innovation
Technology & Digital
Technology Consulting might also be referred to as IT consulting. However, the rise of Digital, Fintech and all the Tech Startups activities is changing the rules of the game. The capability has been rejuvenated as most companies have now elevated technology to the highest level of their agenda.
Technology consultants offer services helping companies embrace new technologies, digitize their processes and modernize their legacy systems. In short, leverage technology as a source of competitive advantage. The scope for this activity overlaps with strategy and functional areas for strategy, media, and specific systems and with IT services for the low end/recurring activities. Depending on definitions the category can represent up to one-third of the global consulting market.
The category includes capabilities such as Digital Strategy, Digital Architecture, Systems Integration (CRM, ERP, …), Data Management and Analytics, Cyber Security, or IT related services.
What Are the Roles of a Management Consultant?
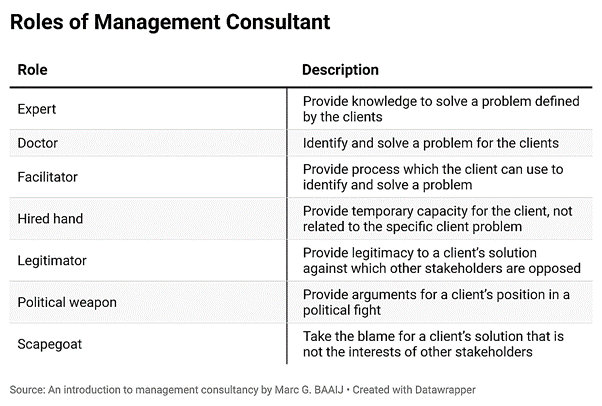
What Do Consultants Do?
“Anybody saying a management consultant solves ‘business problems’ either over-simplifies it or doesn’t know much about consulting!” – Hélène Laffitte
The types of work you’ll be doing as a Consultant can be split into the below categories:
- Practice or Business Development Work (non-billable)
- Client Work (billable)
- Admin tasks (non-billable)
- Personal Development
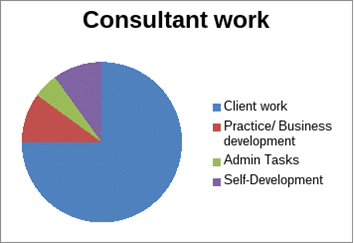
Normally, a consultant would largely dwell on client-facing work. Having Projects on his/her plate to accomplish those by the deadlines.
Client Work
The first and foremost part for which consultants are hired by the clients is to do the Client-Work.
- First task is Data Gathering/ Data Collection and it’s actually much harder than it sounds. You’re trying to find specific sets of data to base a recommendation on. The types of data gathering that you’ll end up doing are Primary and Secondary Research by yourself.
Primary Research would include a questionnaire or interviewing the employees by preparing a workshop. In secondary research you’re looking at data that already exist like surfing the internet or looking through company reports. Often, your firm would have external research that they use like “GARTNER”, “FORRESTER”.
- Once you have all this data you need to analyze it. Some examples of analyzing work that you’ll be doing include looking at interview answers and trying to categorize them into key insights or building financial models of financial data.
- After the data gathering and analysis, you need to convert it into something really simple and really easy to understand for your clients. Typically your manager would create a structure for your deliverables and you’ll be asked to create content for it.
- Now comes the client presentation, you’ll be presenting back what you’ve learned as you’re often the person who’s done most of the groundwork.
Below is a chart that shows the example of client problem and how they ask consultants to overcome it.
The chart is categorized into two parts which are:
- Strategic level
- Operational level

Practice/Business Development Work
These are the activities that help to create long-term value for your firm and help to outperform its competitors. Think of this as extracurricular activities you used to do at school but now just in the workplace. This helps your performance review at the end of the year also expand your network.
There are three types of activities you can do:
- Internal-facing activities:
- You develop thought leadership (position, papers, surveys, etc.)
- You develop innovative offerings / productize existing offers.
- You support business development efforts (networking, outreach, etc.)
- You work on proposals.
- You organize internal meetings to share knowledge, train newcomers)
- External activities: (market facing) :These could be anything to do with thought leadership articles to attending conference to push your brand out into the market.
- Business development/Relationships management: This is to help build and manage relationships with your clients. These activities include working on proposals for new clients, even creating, let’s say, trend reports. This type of work you usually do on top of your daily work.
Admin Tasks
Admin tasks would generally take up 10% of your time which includes logging in into your timesheets for your work hours, Expense reports, and HR stuff (Objectives, reviews, Career etc.). If you’re doing the client work, the admin tasks would be like scheduling meeting rooms to finding post-it notes and printing of materials for workshops.
These are small tasks so try to get them right for the starters. This allows you to gain more trust and more responsibilities from your team.
Personal Development
There’s always room for improvement. These include training, reading, learning new cases and getting more ideas about the project. Some would allocate 10% of their time into these activities and some would just skip it. But, in order to grow, self-development is a necessary task that consultants do while working on their respective projects.
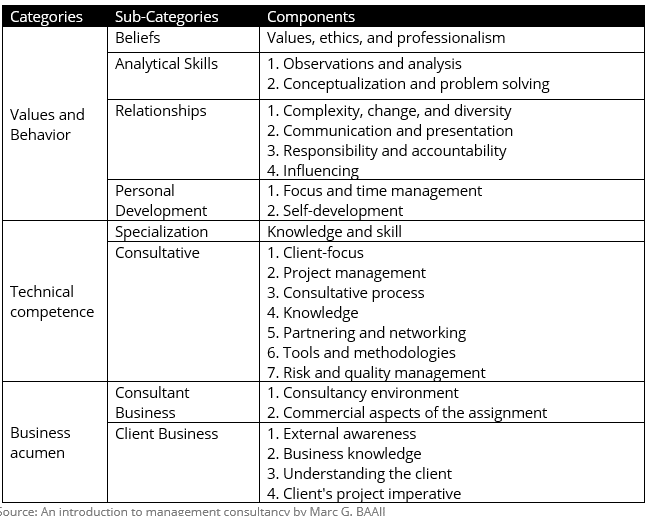
The Activities & Competencies of a consultant:
Management Consultants play various roles and need to have different competencies in order to get the projects done and move up in the career ladder. Below are two tables that showcase the various roles and competencies that a management consultant has to play and have respectively.
Core Competencies of a Management Consultant by ICMCI
Conclusion
Management consulting is a great industry with many exceptional qualities. Its salaries are varied by hardly any other industry, and opportunities for upward movement abound. While the work environment is competitive, we believe it’ll drive you to be the best that you can be. Additionally, management consultancy can be great in moving forward in your career ladder.
Author

Improveo Editorial Team
We handpick for you a wide variety of Case studies, White papers, Insights, Videos to help you to stay current, learn and get improvement ideas for your business. You define in your settings, your centres of interest and we do our best to help you to discover new content in your
Capabilities
Human Capital, Digital, Technology & Data, Risk & Compliance
Industry
Agriculture, Professional Services
Language
English
Location
Asia, Europe, Latam, Africa, North America, Oceania, Middle East
Type
Official

0 Comment